Neural Networks
Neural networks are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) model. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes, or "neurons," that process information and make decisions based on that information. They are universal function approximators, meaning they are capable of approximating any function, given enough data, computing power and of course a network architecture as well as hyper parameter choices that fit the problem. This property makes them highly versatile and adaptable to a wide range of applications, as they can learn to model complex relationships between inputs and outputs, without requiring explicit rules or programming. This also makes them ideal for tasks such as pattern recognition, data classification, and regression analysis.
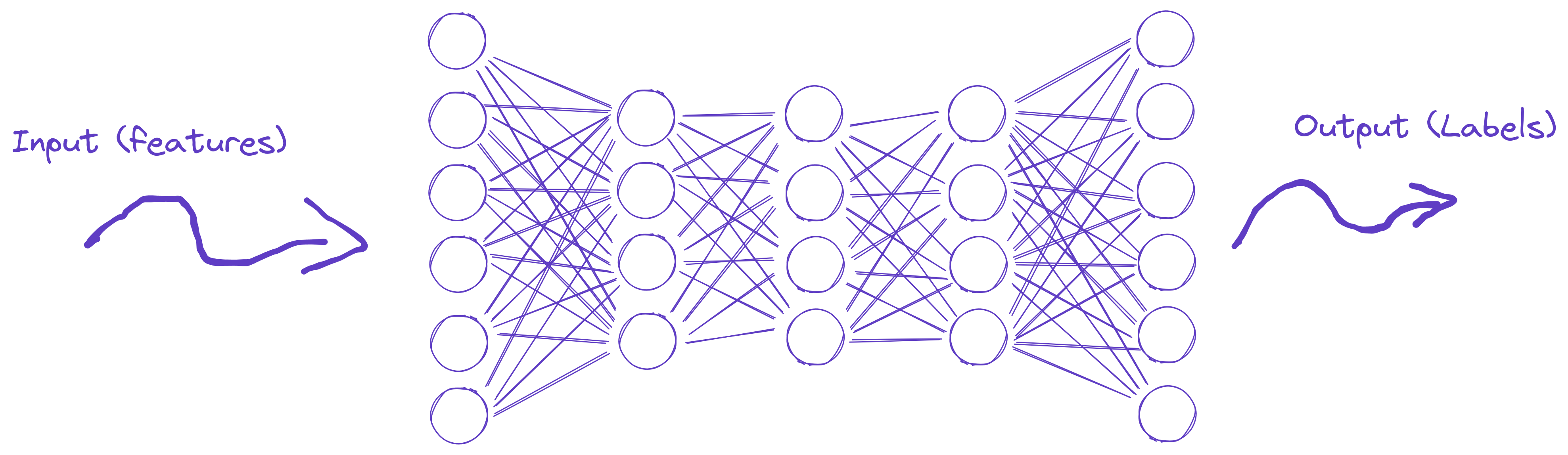
A basic neural network can be visualized by nodes and vertices:
At a high level, a neural network can be seen as a set of interconnected mathematical functions, where each node or neuron performs a simple computation on its inputs and passes the result to the next layer of neurons.
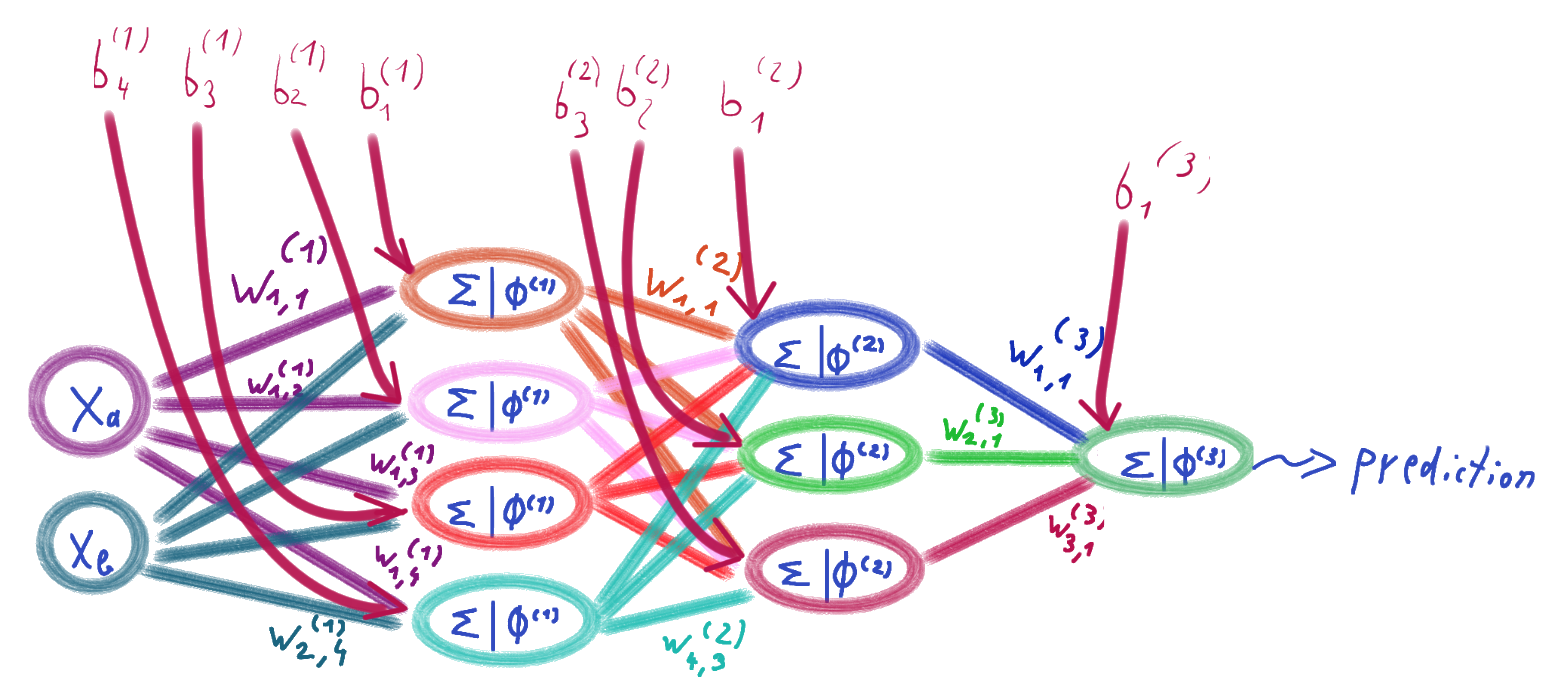
The basic building block of a neural network is the perceptron, which is a single neuron that takes a set of inputs, multiplies each input by a weight, sums the weighted inputs, adds a bias term, and applies a usually non-linear function to produce an output. The mentioned function is also called <em>activation function</em>.
A neural network consists of multiple layers of perceptrons, each layer performing a different set of computations. The input layer receives the raw input data, while the output layer produces the final output of the network. In between, there can be one or more hidden layers, which allow the network to model complex nonlinear relationships between the inputs and outputs.
The weights and biases are learned during training, through a process called backpropagation, which involves computing gradients and updating the parameters to minimize a loss function that measures the difference between the predicted output and the true output.
The activation function is a key component of a neural network, as it introduces nonlinearity into the model and allows the network to learn more complex patterns. Common activation functions include the sigmoid function, the ReLU function, and the softmax function, which are applied element-wise to the output of each neuron.
The following draft visualizes the components of a neural network. The inputs are denoted by , weights by , biases by , activation functions by , and refers to the sum which is calculated over the product of each input weight times input value.